
Hepatocellular carcinoma serum derived exosomal HIF-1α induces phosphoinositide-3 kinase/protein kinase B signaling to induce the angiogenesis and proliferation of HCC
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common malignant tumor of liver, with the third highest incidence and mortality rate in the world (1). The majority of patients with HCC succumb largely died of recurrence and metastases in one year. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) family serve important role in HCC metastasis including epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (2), invasion of the extracellular matrix, intravasation, extravasation and secondary growth of metastases (3). Highly expression of HIF-1α means poor prognosis for clinical outcome in HCC patients (4) and is prone to resulting in metastasis (5,6). Many reports have described HCC metastasis was closely associated with glucose metabolism, and HIF-1α signaling may serve an essential role (7-9). HIF-1α stabilization may drive aerobic glycolysis in HCC (10). HIF-1α also recruits suppressive and pro-angiogenic T-cell subsets by the selective chemokine secreted from tumor and vascular cells (11,12). Thus, HIF-1α not only exerts effects on HCC tumor but also on the HCC microenvironment.
Exosomes are small lipid-bilayer vesicles secreted by many different cell types, including tumor cells. They play role in tumor development and metastasis (13,14). DNA, mRNAs, noncoding RNAs, and proteins take exosome as a cargo to make phenotypic changes in target cells (15-17). He et al. (18) revealed that exosomes isolated from metastatic HCC cell lines were apt to increase the migratory and invasive abilities in normal hepatocytes. However few studies have been reported of the effects of HCC serum-derived exosomes on HCC cells.
The HCC serum-derived exosomes with HIF-1α expressed highly were identified and co-incubated with human umbilical endothelial cells (HUVECs) and Huh7 cells. HCC serum-derived exosomes may promote angiogenesis and proliferation via the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway in in vivo and in vitro experiments. It may offer novel potential therapeutic strategies targeting HCC angiogenesis and proliferation.
Methods
Patients
Serum samples from patients with HCC (n=48) and healthy individuals (n=24) were obtained from Jiangsu Cancer Hospital (Nanjing, China). Research procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee of Jiangsu Cancer Hospital, for clinical research and all patients signed written informed consent for biomedical research. The diagnosis of HCC was performed using histological samples and/or by combining clinical, biochemical and radiological analyses according to the European Association for the study of the liver guidelines, and staging was determined according to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) system.
Cell lines
The hepatic tumor cell lines Huh-7 and HUVECs were cultured with 37 °C under a 5% CO2 humidified environment in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with high glucose (HyClone; GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Logan, UT, USA) and 10% fetal calf serum (FCS; Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), or DMEM low glucose media with 10% FCS respectively. The two cell lines were purchased from Wuhan Institute of Cell Biology, China Center (Wuhan, China). Mycoplasma was tested negative in all cells prior to the experiments.
Exosome isolation and purification
The present study used Total Exosome Isolation reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) to precipitate exosomes. The purified exosome samples were washed thrice with PBS. To analyze the protein in exosome, samples were suspended in exosome-depleted PBS and then assessed using a BCA protein assay kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, China).The exosomes were kept at −80 °C and used no more than 7 days following isolation.
Assessment of exosome size and distribution in serum samples
Serum exosomes were resuspended in 100 µL of pre-filtered PBS and analyzed by Zetasizer Nano ZS90 (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK) equipped with a monochromatic 465 nm laser. Datas were processed by the particle-tracking software (Zetasizer Ver 7.03, Malvern Instruments, Ltd).
Transmission electron microscopy
Prepared exosomes were immobilized with 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 2 h. Twenty µL exosomes were put on a formvar/carbon-coated grid. Purified exosomes were negatively stained with 3% aqueous phosphotungstic acid for 2 min and viewed with transmission electron microscope at 80 kV (JEM-1230; JEOL, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
Exosome labeling
Exosomes from HCC patients were labeled using PKH67 (green) membrane-binding fluorescent labels (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Labeled exosomes were washed with DMEM, collected by ultracentrifugation and resuspended in DMEM with low glucose. HUVECs were incubated at 37 °C with 200 µg/mL of PKH67-labeled exosomes for 6 h. The samples were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, washed three times with PBS. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst in 20 min and fixed with PBS glycerol. Image collection was performed with TCS SP-5 confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). Images were collected with scanning rate of 400 Hz with resolution of 512×512 pixels, image analysis was conducted using Leica Application Suite 2.02 (Leica Microsystems GmbH).
Protein analysis
A total of 50 or 100 µL of serum-derived exosomes from HCC patients or healthy individuals were lysed in 50 µL of Radioimmunoprecipitation Assay (RIPA) buffer (Nanjing KeyGen BioTech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China).We quantified exosomal protein concentration by the BCA Protein Assay kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology).
Western blot assay
Equal quantities of proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes and blocked with 5% non-fat milk. Cells were collected and washed twice with chilled PBS, and dissolved in RIPA buffer (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA). For western blot analysis, anti-cluster of differentiation CD-63, anti-CD9 (1:1,000; Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), anti-HIF-1α (1:1,000; Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), anti-Flotillin-1, anti-AKT and anti-phosphorylated -AKT (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) were used. β-actin (1:2,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) was used as house-keeping genes in Western blot assays. The expressed proteins were checked and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Gel-Pro Analyzer (Media Cybernetics, USA). HRP-conjugated Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG, HRP-conjugated Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (1:1,000; Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) were used as secondary antibodies.
Flow cytometric cell cycle analysis
HUVECs were collected at 48 hours with different types of exosomes in 6 cm plates. Cells were harvested using cold PBS and fixed with 70% cold ethanol for 24 hours at −20 °C and treated with 1 ng/mL RNaseA for 20 minutes at 4 °C. A total of 0.5 mg/mL propidium iodide (50 mg/mL; Becton, Dickinson and Company, Franklin, Lakes, NJ, USA) was used to stain the cellular DNA in the dark for 20 minutes at 4 °C. HUVECs were categorized by FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer (Becton, Dickinson and Company) and CellQuest acquisition and analysis programs (Becton, Dickinson and Company). All procedures were repeated three times.
Tube formation assay
A total of 2×104 HUVECs were plated in 96-well plates on top of matrigel, treated with exosomes cultured for 24 hours. Tube networks were quantified with per pixel length acquired with image analysis of 5 random microscopic fields by ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Cell viability assay
Cell viability was obtained by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). Cells were embedded into 96-well plates, grown to 50–60% confluence for 12 hours. Following treatment under different conditions, we mixed 10 µL of CCK-8 reagent in each well culture medium containing 100 µL and incubated cells for 1.5 hours at 37 °C. We used Fluorescence Spectrophotometer (Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) to read the optical density (OD) of each well at 450 nm.
Wound-healing assays
For wound-healing assays, we monitored the cell migration for 24 h by using the 100 µL micropipette tip to scratch the confluent HUVECs monolayers incubated with or without exosomes. We calculated the widths of the wound by ImageJ software (http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/), measured and the percentage of wound healing by the formula: 100% − (width after 24 hours/width at the beginning) × 100%.
Detection of HIF-1α by ELISA
The concentration of exosomal HIF-1α was acquired by ELISA kits (HIF-1 ELISA kit, cat. No. CSB-E12112h; CusAbio, Wuhan, China). The OD of each well was read in a Fluorescence Spectrophotometer (Hitachi, Ltd.) at 450 nm. Analyses were repeated in duplicate.
Animal xenograft tumor model
Experiments mice were used with the permission and consent of the Animal Care and Use Committee and Animal Center of Nanjing Medical University (Nanjing, China). 20 BALB/c nude mice (4–6 weeks old) were bought from Shanghai Animal Center (Shanghai, China). The nude mice were kept at a temperature of 20–25 °C and housed in a relative humidity of 30–60% with standard rodent chow and water for freedom in the light controlled vivarium (14 hours light and 10 hours darkness). About 6-weeks-old male nude mice were implanted subcutaneously near the forepaw with Huh-7 cells (1×106, 100 µL) and were randomly assigned to three groups (7 animals in HCC-ex or normal-ex group and 6 animals in control group). Exosome therapy was carried out following 1 week of tumor cell inoculation; 20 µg of exosome protein was dissolved in PBS and injected into the area around the tumor 3 times a week for 1 month. When primary visible tumors appeared, the tumor size, mice weight and health were measured daily. Mice were sacrificed 1 month following tumor injection, in vivo tumors were isolated, weighed and subjected to immunohistochemical assays using the anti-CD31 antibody (1:40; Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd.).
Microvessel density (MVD) assessment
We stained vascular endothelial cells with CD31 (PECAM-1), and calculated the CD31-positive MVD. We selected five areas with the highest number of hot spots, and counted the number of vessels at a high-power magnification (×200).
Statistical analysis
We performed each experiment at least three times. Results were recorded as the mean ± standard deviation. We analyzed the differences between groups by ANOVA analysis and Student’s t-test. All P values were based on a two-sided statistical analysis. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001).
Results
Characterization and concentration of serum exosomes from patients undergoing HCC and healthy individuals
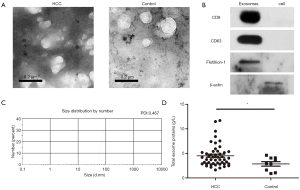
Serum exosomes were observed by transmission electron micrographs. These vesicles exhibited cup-shaped morphology (Figure 1A) and a high concentration of the exosome protein markers CD9, CD63 and Flotillion-1 was observed following western blot analysis (Figure 1B). Nanoparticle tracking analysis of isolated serum HCC exosomes revealed that the size distribution was in accordance with the expected size range of exosomes (~58 to 164 nm; number mean: 83.16 nm; PDI: 0.467, Figure 1C). In addition, the exosome concentration was higher in patients suffering HCC when compared with controlled group (Figure 1D). Tables S1 and S2 summarize the characteristics of the healthy individuals and patients.
HCC-exosomes promote tumor angiogenesis and proliferation in vitro
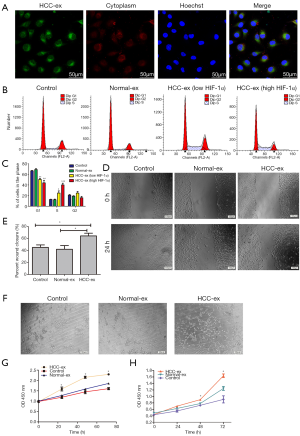
The present study demonstrated the transport of exosomes from HCC patients into HUVECs using the method modified from Umezu’s reports (19). Following incubation with PKH67-labeled exosomes from HCC patients, the PKH67 signals were colocalized in the cytoplasm of HUVECs (Figure 2A). Flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that the HCC exosomes decreased the percentage of cells in the G1 phase (50.50%±1.91% and 43.99%±4.81% vs. 66.55%±0.79% and 69.11%±1.67%, respectively; P=0.0005) whereas there was a rising percentage of cells in the S phase (24.75%±3.99% and 40.09%±3.26% vs. 12.69%±0.47% and 12.20%±1.11%, respectively; P=0.0002; Figure 2B,C). HCC exosomes especially high HIF-1α exosomes could promote cell proliferation and cell cycle arrest. In addition, HUVECs cocultured with high HIF-1α exosomes exhibited an increase in the percentage of cells in the S phase and a decrease percentage of cells in the G1 phase when compared with the low HIF-1α exosomes from HCC patients (40.09%±3.26% vs. 24.75%±3.99%; 43.99%±4.81% vs. 50.50%±1.91%, respectively; P<0.05; Figure 2B,C). Wound healing was significantly increased by HCC-exosomes compared to the control group following 24 h (Figure 2D,E). HUVECs cultured with HCC-exosomes promoted the tube formation of HUVECs while healthy individual exosomes and controls did not (Figure 2F). We found HCC-exosomes (200 µg protein) increased the proliferation of HUVECs and Huh-7 cells when compared with the control or normal exosomes (Figure 2G,H) by CCK-8 assays.
HIF-1α level in exosomes is upregulated in HCC and exosomal HIF-1α induces PI3K/AKT signaling to induce angiogenesis
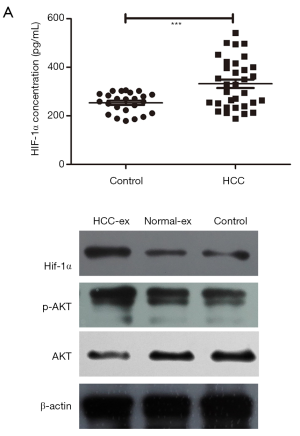
HIF-1α level in exosomes was higher in HCC patients (332.38 pg/mL) compared with the healthy individuals (253.9 pg/mL; P=0.0007; Table 1). Upon clinical features correlation analysis, exosomal HIF-1α overexpression was closely associated with BCLC stage (P=0.031; Figure 3A). Figure 3B and Tables S1,S2 summarize the patients’ characteristics. Exosomes incubated with HUVECs cells had increased PI3K/AKT and kept no difference in the recipient cells, potentially indicating that HCC-exosomes transfer HIF-1α via exosomes to HUVECs by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (Figure 3B).
Table 1
| Clinical features | No. of cases without exosomal HIF-1α overexpression | No. of cases with exosomal HIF-1α overexpression | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.699 | ||
| Male | 13 | 12 | |
| Female | 5 | 3 | |
| BCLC stage | 0.031* | ||
| B | 14 | 6 | |
| C | 4 | 9 | |
| Tumor size (cm) | 0.166 | ||
| <5 | 11 | 5 | |
| ≥5 | 7 | 10 | |
| Venous invasion | 0.239 | ||
| Absent | 15 | 6 | |
| Present | 3 | 6 |
*, statistical analyses were performed by the Pearson χ2 test. P<0.05 was considered significant. HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
HCC serum-derived exosomes accelerate xenograft tumor proliferation and angiogenesis
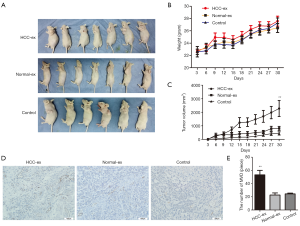
The present study performed an HCC xenograft model by injecting different types of exosomes into nude mice. Consistent with the present aforementioned results, exosomes from HCC patients appeared to accelerate tumor proliferation compared to healthy individuals or control group (P=0.007; Figure 4A,B,C; 2,278±589.8 vs. 812.4±147.9; P=0.0329; 2,278±589.8 vs. 438.7±119.5; P=0.0164). In addition, mice injected with high levels of exosomal HIF-1α from HCC patients had promoted vascularization (P=0.0042; Figure 4D,E). Overall, these results may indicate that HIF-1α accelerates the growth of HUVECs via exosomes, and enhanced tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis.
Discussion
Proteins, RNAs and other types of molecules involved in the pathology of cancer were carried by exosomes (13,20). Colon cancer cells contain microRNAs (miRNAs) secreted exosomes involved in cancer progression and mediated by the major vault proteins that sort miRNAs (21). Tumor-associated macrophage-derived exosomes transferred functional Apolipoprotein E to promote the migration of gastric cancer cells (22). Recently, many studies were conducted to reveal the role of exosomes in HCC angiogenesis and proliferation (15,23,24). In the present study, the exosomal concentration in HCC patients and healthy donors was analyzed. We found the HCC patients exhibited a greater capacity to convert HIF-1α in serum exosomes than healthy individuals, and high serum exosomal HIF-1α levels were correlated with the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which promoted xenograft tumor proliferation and angiogenesis. Liu et al. (25) reported that HIF-1α induced a phenotypic switch in human vascular smooth muscle cells through PI3K/AKT/astrocyte elevated gene-1 signaling. Furthermore, we indicated that high HIF-1α expression in serum exosomes is correlated with the BCLC stage of HCC, which has important implications for efficient prevention and therapeutic strategies. This was consistent with the results of the Li et al. (26) study, which demonstrated that co-expression of HIF-1α and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8 was a prognostic factor in HCC.
HCC is considered to be a dynamic model of the associations between the tumor microenvironment and tumor intercellular communications (27). In addition, there is emerging evidence that has indicated that hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment promotes tumor angiogenesis and proliferation (28). Tumor-derived exosomes hold important role in the intercellular communications and angiogenesis associated with the tumor environment (29). Therefore, study of the interactions between the tumor microenvironment and angiogenesis, and proliferation mediated by exosomes is required. Exosomes identified from the serum of HCC patients may be a vital component of HCC microenvironment.
The HIF-1α/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in malignant tumors is not a novel concept. Many studies have indicated that HIF-1α in the exosomal pathway under hypoxic conditions secretes several growth factors to stimulate PI3K signaling activation (30). The HIF-1α/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway of oral squamous cell carcinoma may contribute to the anti-carcinogenic activity of Sal-B (31). In the present study, the HIF-1α/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway mainly contributed to the angiogenesis and proliferation in HCC.
In conclusion, the present results indicated that HCC serum derived exosomes activated HUVECs by increasing HIF-1α/PI3K/AKT signaling in HCC. In addition, HCC patients exhibited a greater capacity to convert HIF-1α in serum exosomes than healthy individuals, which could promote xenograft tumor proliferation and angiogenesis. Notably, high expression of HIF-1α in serum exosomes exhibited a positive correlation with BCLC stage in HCC patients. The present study may elucidate a molecular mechanism underlying the crosstalk between HCC cells and exosomes to promote angiogenesis and proliferation.
Table S1
| Variable | Sample | Age (y) | Sex (0: male; 1: female) | Serum HIF-1ɑ levels in exosomes (pg/mL) | Serum exosome concentration (µg/μL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort of serum exosome concentration | 1 | 32 | 0 | 270.071 | 1.61574 |
| 2 | 42 | 0 | 250.244 | 2.904544 | |
| 3 | 45 | 0 | 223.031 | 1.05877 | |
| 4 | 48 | 0 | 287.376 | 4.070296 | |
| 5 | 39 | 0 | 268.144 | 4.627266 | |
| 6 | 34 | 1 | 302.856 | 2.885114 | |
| 7 | 37 | 0 | 270.071 | 0.9098124 | |
| 8 | 41 | 0 | 305.027 | 4.102678 | |
| 9 | 50 | 1 | 186.007 | 3.565136 | |
| Cohort of serum HIF-1ɑ levels in exosomes | 10 | 47 | 0 | 302.931 | – |
| 11 | 40 | 1 | 195.701 | – | |
| 12 | 36 | 1 | 279.541 | – | |
| 13 | 36 | 0 | 295.836 | – | |
| 14 | 38 | 1 | 258.989 | – | |
| 15 | 42 | 1 | 290.365 | – | |
| 16 | 44 | 0 | 188.644 | – | |
| 17 | 31 | 1 | 243.608 | – | |
| 18 | 35 | 0 | 235.875 | – | |
| 19 | 51 | 0 | 258.683 | – | |
| 20 | 47 | 1 | 204.702 | – | |
| 21 | 55 | 1 | 283.817 | – | |
| 22 | 37 | 0 | 179.351 | – | |
| 23 | 49 | 1 | 302.593 | – | |
| 24 | 32 | 1 | 210.876 | – |
HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor.
Table S2
| Variable | Sample | Age (y) | Sex (0: male; 1: female) | Tumor size (0: ≤5 cm; 1: >5 cm) | BCLC stage (1: A; 2: B; 3: C stage) | Venous invasion (0: none; 1: presence) | Serum exosome concentration (µg/μL) | Serum HIF-1ɑ levels in exosomes (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort of serum exosome concentration | 01 | 63 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 4.43945 | 350.184 |
| 02 | 47 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 9.516948 | 265.127 | |
| 03 | 42 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5.372052 | 264.266 | |
| 04 | 59 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2.846256 | 218.626 | |
| 05 | 87 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4.931657 | 298.5 | |
| 06 | 59 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2.308715 | 271.378 | |
| 07 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 11.49225 | 294.68 | |
| 08 | 69 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2.949878 | 255.244 | |
| 09 | 55 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5.410911 | 452.049 | |
| 10 | 61 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3.183029 | 362.828 | |
| 11 | 36 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3.732407 | 389.292 | |
| 12 | 58 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2.682166 | 444.908 | |
| 13 | 30 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2.871905 | 328.89 | |
| 14 | 41 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2.475503 | 354.431 | |
| 15 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2.184215 | 254.555 | |
| 16 | 51 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2.868341 | 397.25 | |
| 17 | 84 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2.442544 | 377.628 | |
| 18 | 79 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4.343488 | 416.774 | |
| 19 | 42 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7.406912 | 400.933 | |
| 20 | 33 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4.88687 | 422.935 | |
| 21 | 47 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 4.193836 | 233.529 | |
| 22 | 84 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3.177445 | 234.68 | |
| 23 | 32 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5.155888 | 500.594 | |
| 24 | 53 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3.727062 | 495.199 | |
| 25 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4.233921 | 541.786 | |
| 26 | 61 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6.370034 | 212.567 | |
| 27 | 29 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4.714056 | 497.536 | |
| 28 | 48 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3.639765 | 188.795 | |
| 29 | 80 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3.140923 | 208.941 | |
| 30 | 82 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2.013184 | 329.68 | |
| 31 | 50 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5.939783 | 239.554 | |
| 32 | 76 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4.689115 | 213.839 | |
| 33 | 69 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2.796187 | 251.566 | |
| Cohort of serum HIF-1ɑ levels in exosomes | 34 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3.734189 | – |
| 35 | 65 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7.545876 | – | |
| 36 | 60 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1.634598 | – | |
| 37 | 61 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3.268306 | – | |
| 38 | 44 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3.062533 | – | |
| 39 | 51 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 7.126314 | – | |
| 40 | 58 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 8.434883 | – | |
| 41 | 60 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4.258863 | – | |
| 42 | 58 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4.032603 | – | |
| 43 | 47 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5.198646 | – | |
| 44 | 41 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 11.68894 | – | |
| 45 | 64 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3.748441 | – | |
| 46 | 59 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2.839836 | – | |
| 47 | 49 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2.637627 | – | |
| 48 | 52 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5.447176 | – |
HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Zhao Hui, Ms. Song Jie, and Ms. Sun Meng Ting for their technical assistance. The authors are also grateful to Dr. Yin Rong for his academic advice.
Funding: This work was supported by grants from
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2019.08.07). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013). Research procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee of Jiangsu Cancer Hospital, for clinical research and all patients signed written informed consent for biomedical research.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015;136:E359-86. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Zhang Q, Bai X, Chen W, et al. Wnt/ -catenin signaling enhances hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via crosstalk with HIF-1 signaling. Carcinogenesis 2013;34: [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wilson GK, Tennant DA, Mckeating JA. Hypoxia inducible factors in liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: Current understanding and future directions. J Hepatol 2014;61:1397-406. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Dai CX, Gao Q, Qiu SJ, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha, in association with inflammation, angiogenesis and MYC, is a critical prognostic factor in patients with HCC after surgery. BMC Cancer 2009;9:418-20. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Xiang ZL, Zeng ZC, Fan J, et al. Gene expression profiling of fixed tissues identified hypoxia-inducible factor-1C, isGF, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 as biomarkers of lymph node metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:5463. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Kai AK, Chan LK, Lo RC, et al. Down-regulation of TIMP2 by HIF-1of fixed tissues identified hypoxia-inducible factor-1C, isr metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2016;64:473-87. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Gwak GY, Yoon JH, Kim KM, et al. Hypoxia stimulates proliferation of human hepatoma cells through the induction of hexokinase II expression. J Hepatol 2005;42:358-64. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Kim W, Yoon JH, Jeong JM, et al. Apoptosis-inducing antitumor efficacy of hexokinase II inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 2007;6:2554-62. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sheng SL, Liu JJ, Dai YH, et al. Knockdown of lactate dehydrogenase? A suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS J 2012;279:3898-910. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Tennant DA, Durán RV, Boulahbel H, et al. Metabolic transformation in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2009;30:1269-80. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Noman MZ, Desantis G, Janji B, et al. PD-L1 is a novel direct target of HIF-1HIF-1IF-1is 2009;30s 2009;30;30J 2012lular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Therapeuttol Exp Med 2014;211:781-90.
- Doedens AL, Phan AT, Stradner MH, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors enhance the effector responses of CD8(+) T cells to persistent antigen. Nat Immunol 2013;14:1173-82. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Chen L, Guo P, He Y. HCC-derived exosomes elicit HCC progression and recurrence by epithelial-mesenchymal transition through MAPK/ERK signalling pathway. Cell Death Dis 2018;9:513. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Fu Q, Zhang Q, Lou Y, et al. Primary tumor-derived exosomes facilitate metastasis by regulating adhesion of circulating tumor cells via SMAD3 in liver cancer. Oncogene 2018;37:6105-18. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wang S, Xu M, Li X, et al. Exosomes released by hepatocarcinoma cells endow adipocytes with tumor-promoting properties. J Hematol Oncol 2018;11:82. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Fang JH, Zhang ZJ, Shang LR, et al. Hepatoma cell-secreted exosomal microRNA-103 increases vascular permeability and promotes metastasis by targeting junction proteins. Hepatology 2018;68:1459-75. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Fu X, Liu M, Qu S, et al. Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2018;37:52. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- He M, Qin H, Poon TC, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomes promote motility of immortalized hepatocyte through transfer of oncogenic proteins and RNAs. Carcinogenesis 2015;36:1008-18. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Umezu T, Tadokoro H, Azuma K, et al. Exosomal miR-135b shed from hypoxic multiple myeloma cells enhances angiogenesis by targeting factor-inhibiting HIF-1. Blood 2014;124:3748. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Braicu C, Tomuleasa C, Monroig P, et al. Exosomes as divine messengers: are they the Hermes of modern molecular oncology? Cell Death Differ 2015;22:34-45. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Teng Y, Ren Y, Hu X, et al. MVP-mediated exosomal sorting of miR-193a promotes colon cancer progression. Nat Commun 2017;8:14448. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Zheng P, Luo Q, Wang W, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages-derived exosomes promote the migration of gastric cancer cells by transfer of functional Apolipoprotein E. Cell Death Dis 2018;9:434. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Lin XJ, Fang JH, Yang XJ, et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell-Secreted Exosomal MicroRNA-210 Promotes Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2018;11:243-52. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wang X, Shen H, Zhangyuan G, et al. 14-3-3l. 14-3-3-3-3-3-3. 14-3-3creted Exosomal MicroRNA-210 Promotes Angiogenesis tric cancer cells by tranrating T?lymphocytes. Cell Death Dis 2018;9:159. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Liu K, Fang C, Shen Y, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1a induces phenotype switch of human aortic vascular smooth muscle cell through PI3K/AKT/AEG-1 signaling. Oncotarget 2017;8:33343-52. [PubMed]
- Li XP, Yang XY, Biskup E, et al. Co-expression of CXCL8 and HIF-1ces phenotype switch of human aortic vascular smos in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015;6:22880-9. [PubMed]
- Leonardi GC, Candido S, Cervello M, et al. The tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma Int J Oncol 2012;40:1733-47. (Review). [PubMed]
- De Francesco EM, Sims AH, Maggiolini M, et al. GPER mediates the angiocrine actions induced by IGF1 through the HIF-1 the HIF-1ced by IGF1 through the HIF-1 the HIF-1F-1h muscle cell thro 2017;19:129.
- Abak A, Abhari A, Rahimzadeh S. Exosomes in cancer: small vesicular transporters for cancer progression and metastasis, biomarkers in cancer therapeutics. Peer J 2018;6:e4763. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Kucharzewska P, Christianson H, Welch J, et al. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:7312-7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wei J, Wu J, Xu W, et al. Salvanic acid B inhibits glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma via targeting PI3K/AKT/HIF-1KT/HIF-1K/AKT/HIF-y. Cell Death Dis 2018;9:599. [Crossref] [PubMed]


